Introduction
BIOSLEVEL.com recently looked at Sapphire’s Radeon HD4650 videocard, one of the latest mid-range offerings based on AMD’s ATI brand of GPUs. We were impressed by the features and performance of the card, especially at it’s very moderating pricing.
The folks at Sapphire were kind enough to send their Radeon HD4550 card at the same time, which will be on the table today. The Radeon HD4550 features 512MB of DDR3 memory, a 600MHz core clock, and 80 stream processors. It’s not quite as beefy as the Radeon HD4650, but it can be found for an average of $30 less.
Packaging
The Radeon HD4550 shipped to us in a box roughly half the size of that of their high-end cards we’ve seen in the past. The card’s title is printed nice and large, and a cute female with a rather large sword takes up the rest of the box’s front side. Along with this are the various certifications, as well as Sapphire’s improvements such as PCI-Express 2.0 and 512MB of DDR3.
The back of the box lists several more features and awards, as well as the fact that the cards plays nicely with Vista.
Inside, I found the card packed in nice and securely in a cardboard box. Also inside were a driver CD, component cable, HDMI dongle, and a VGA dongle.
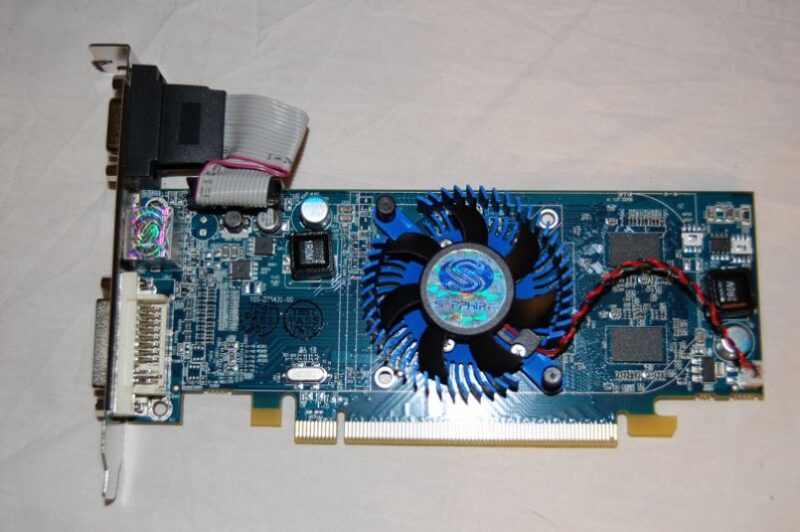
The card itself came wrapped up in the typical anti-static wrap. It’s a small card, and has brackets that fit both low-profile and full-profile systems.
For a mid-range card, I can’t help but call the card sexy. The first thing that stuck out to me was the heatsink and fan, as this isn’t something I’m used to seeing on anything but high-end cards. Alas, even today’s mid-range GPUs require active cooling.
The Radeon HD4550 doesn’t features any DisplayPort connections, but rather a single DVI port and a lone VGA port. People still use VGA connections?!
The back of the card doesn’t necessarily reveal anything special.
Features
- ATI Radeon HD 4550 – 512MB of DDR3 memory
- DirectX 10.1
- 80 stream processing units
- 12x custom filter anti-aliasing (CFAA) and high performance anisotropic filtering
- PCI Express 2.0 support
- Dual mode ATI CrossFireX technology multi-GPU support for highly scalable performance
- ATI Avivo HD video and display technology
- Unified Video Decoder 2 (UVD 2) for Blu-ray and HD Video
- DVD Upscaling & Built-in HDMI with 7.1 surround sound support & Integrated DisplayPort with audio
- Dynamic power management with ATI PowerPlay technology
Specifications
- I/O Output: VGA+DL-DVI-I+HDTV
- Core Clock: 600 MHz & 80 Stream Processors
- Memory Clock: 800MHz, 1800 Mbps.
- PCI Express 2.0 x16 bus interface
- 512MB /64bit DDR3 memory interface
- Single Slot Active Cooler
- HDMI compliant via dongle
- 7.1 Audio Channel Support
- Microsoft DirectX 10.1 support
- Shader Model 4.1 support
More information can be found on Sapphire’s product page.
Installation
There wasn’t much to the installation of the Radeon HD4550. The card merely requires an unused PCI-Express x16 slot, preferably of the 2.0 variety. I’m happy to report that the Radeon HD4550 does not require a PCI-Express power connection. This could be a killer card for many low-powered systems.
Test System
I’m straying a little from my usual bench system due to some flaky hardware. This time around, I’ll be using an Intel Core2 Quad system. Despite a different system, the system will still be running both Windows Vista Business 64-bit with Service Pack 1 and Gentoo Linux 2008.0 64-bit. I’ll look at some of the latest games in Windows, and look at a few similar benchmarks in Linux including results from the Phoronix Test Suite.
| Component | Part | |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Intel Core2 Quad Q6600 | |
| Motherboard | ASUS P5EWS Professional | |
| RAM | 2GB Patriot DDR3-1333 | |
| Video Card | Sapphire Radeon HD4650 | |
| Chassis | Thermaltake M9 | |
| CPU Cooling | Scythe Mugen | |
| Hard Drive | 2x WD Raptor 36GB | |
| Power Supply | NorthQ 850W Black Magic | |
| Display | 1280×1024 | |
| Operating System | Windows Vista Business SP1 64-bit / Gentoo 2008.0 64-bit | |
That said, I’ll be able to compare the Radeon HD4550 against several videocards BIOSLEVEL has reviewed in the past, but I’ll have to be careful with any conclusions due to the fact that I’m using different hardware. Let’s get started with the Windows benchmarks. I’ll be looking at performance in Cinebench, 3dMark06 and Vantage, Unreal Tournament 2004, Unreal Tournament 3, Crysis, Quake 4, and Half-Life 2.
Windows Benchmarks
I started off the benchmarking process with some of our typical gaming benchmarks. Once again, I’m testing with Windows Vista 64-bit with Service Pack 1. As we’ve seen with previous reviews, Windows Vista really hits hard when it comes to gaming performance. The 32-bit version shows decrease in FPS in most games, but the 64-bit version shows an even greater decrease. Many of these cards we test with are capable of much higher framerates, but, well… it’s 64-bit Vista.
I have some animosity towards Vista, having lost my workstation’s hard drive a few months ago. In the future, BIOSLEVEL.com may try to deviate away from Windows benchmarks all together. This will both increase the focus of our site, as well as giving us more time to work with the products in Linux while under deadlines.
Unreal Tournament 2004
Since a Linux port of Unreal Tournament 3 has yet to be released for Linux, I use Unreal Tournament 2004 as a benchmark to compare Linux and Windows performance from videocards and processors. Although an older game, the framerate is still a good determining factor of how good a videocard is. I tested Unreal Tournament 2004 with everything set the maximum settings, at our default resolution, 1280×1024. I’m also using the OpenGL rendering engine, as that is the only available engine i
n Linux. It’s important to note that with Vista, users are stuck with OpenGL 1.5. Higher versions are merely emulated.
Unreal Tournament 3
Despite there not yet being a Linux port, Unreal Tournament 3 is one of the latest PC games out and uses the powerful Unreal Engine 3. Games such as Bioshock, Turok, and others also use this engine, making Unreal Tournament 3 a great benchmark to give an idea how these games will perform as well. This game is using the DirectX 10 engine.
Crysis
Is one of the latest, cutting-edge games. Additionally, Crysis has a 64-bit port whereas Unreal Tournament 3 does not. I found gameplay to be mostly unplayable with anything higher than the default medium settings. I’m attributing this to an issue with the 64-bit version of Vista. Microsoft’s 64-bit operating system just doesn’t seem ready for the prime time yet. This is another DirectX 10 game.
Windows Benchmarks, Continued
Quake 4
Like Unreal Tournament 2004, Quake 4 is a slightly older engine. It remains relevant in that many games still use the engine such as Doom 3 and Quake Wars, and it also has a Linux port. Quake 4 was benchmarked using the highest settings available. The game utilizes OpenGL in both Linux and Windows.
Half-Life 2
Half-Life 2 remains one of the most popular game engines due to the various “Source” games Valve has released, such as Counter-Strike: Source. Additionally, many incremental updates have been added to the game with the episode-style updates Valve released for the game. Half-Life 2 was benchmarked with both Episodes installed, and all settings set to the maximum available.
3dMark06
The benchmark is about two years old now, but still an effective way to look at a video card’s performance.
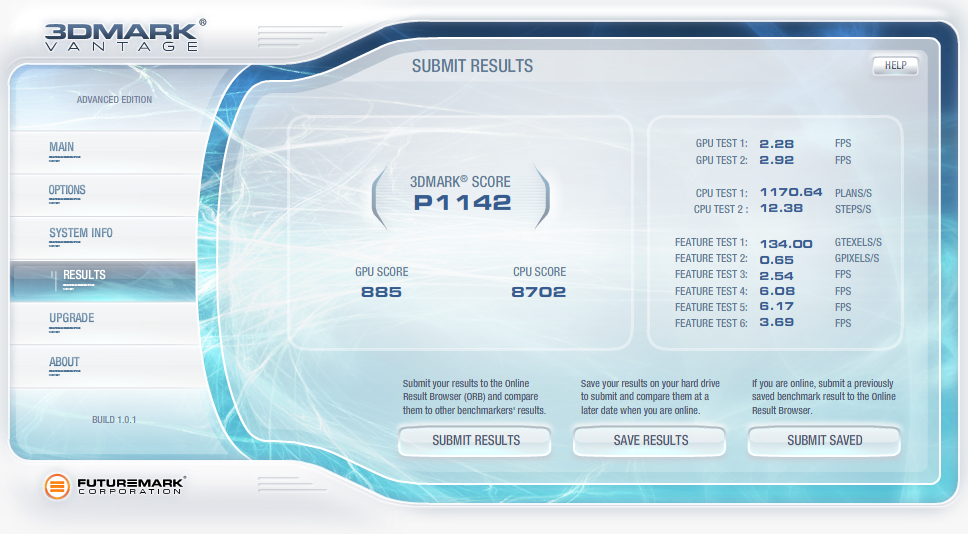
3dMark Vantage
Futuremark’s latest gaming benchmark is the pinnacle of gaming benchmarks and technology, as it may very well bring any setup to its very knees. Through a series of DirectX 10.1, Physics, and CPU tests, 3dMark Vantage measures every ounce of performance that a system is capable of, in every area the latest games utilize.
Cinebench
I’ve decided to add a new Windows benchmark to the mix, Maxon Cinebench. Cinebench is based on Maxon’s Cinema 4D animation software, which is used extensively by studios and production houses worldwide for 3D content creation. On top of this, Maxon has a 64-bit version of Cinebench, perfect for my purposes. Cinebench tests a videocard’s OpenGL rendering performance.
Conclusion on Windows Benchmarks
At first look, the HD4550 isn’t overly impressive on it’s own. However, when considering that it’s a lower-midrange card, the performance might look a little better. The card is capable of handling many popular games, and for it’s price range, a good investment for those building entry-level gaming rigs.
It doesn’t quite meet the performance of the GeForce 9600GSO or Radeon HD4650, but it holds its own place.
Linux Benchmarks
As mentioned in previous reviews, I’m using Gentoo Linux 2008, mostly because I’m more comfortable in a Gentoo environment, but also because the software is compiled specifically to your machine’s specifications (or the best available for the machine, anyways). The operating system has been compiled as 64-bit, so it’ll be interesting to see how some of these benchmarks compare to their Windows counterparts.
For Linux, I’ll be look at Unreal Tournament 2004, Quake 4, glxgears, and Nexuiz. Nexuiz will be tested using the Phoronix Test Suite. The other games will be tested with the same settings as in Windows.
Unreal Tournament 2004
With the 64-bit version of UT2004 installed in Linux as well, I set the settings to the maximum and ran a botmatch on DM-Rankin.
Quake 4
Much like the Windows version, I had everything set to the maximum.
glxgears
glxgears is a simple benchmark included on most distros by default. Although not always a fantastic judge of performance, glxgears can give you a ballpark estimate on how well your video card will perform.
Nexuiz
Nexuiz is a popular open source first person shooter based on a modified (and very advanced) Quake 1 engine. Phoronix recently release a test suite, consisting of some of the benchmarks they commonly use when benchmarking hardware, and it’s all automated through PHP scripts. I opted to run Nexuiz through their benchmark system to standardize the results.
Conclusion on Linux Benchmarks
I have to say that the benchmark numbers in Linux came as a bit of a surprise. The card wasn’t far behind the Radeon HD4650, but still fell behind the numbers we got from the GeForce 9600 and 8800 series cards.
As always, it’s well known that that AMD’s Linux driver isn’t the best. For proof, once can compare similar games in bot Linux and Windows and see where the card falls behind in Linux. That’s partially the purpose of the review to look at how well AMD has implemented their driver.
Final Thoughts & Conclusion
Sapphire’s Radeon HD4550 pulls its weight, despite being a mid-range card. The card doesn’t fall far behind the Radeon HD4650 in terms of performance, and is priced slightly lower. On top of this, the card can fit both low-profile and full-profile systems. This makes for an ideal card for small-profile workstations or DVRs.
Linux performance wasn’t particularly what I would have liked to have seen, but to be fair, it did perform as well as it performed in Windows. nVidia-based cards typically always perform above and beyond AMD cards in Linux, but this can usually be blamed on AMD’s graphics driver in Linux. AMD has promised further improvements to the drive, so it’s only a matter of time before we see equal performance in both Linux and Windows from ATI cards.
Sapphire definitely has a great mainstream card on their hands with the Radeon HD4550 overclocked. With DDR3 memory and the adjustable profile size, the card is sure to be a hit in the mainstream market, especially as the card is capable of playing today’s latest games. For the price, performance, and usability of this card, we’ve awarded it our “#1 Recommended” award.
Pros
- PCI-Express 2.0 Support
- Great pricing point
- DDR3 RAM
- HDCP / HDMI compliant for watching HD movies on HD displays
- Unique and efficient cooler
- Adjustable form factor
- No external power required
Cons
- Linux performance isn’t great